
Navigating the complexities of the cryptocurrency market and seizing opportunities require a blend of innovation, ethical practices, and a deep understanding of distributed ledger technology (DLT).
As blockchain technology reshapes the traditional finance sector and pioneers the expansion of decentralized finance (DeFi), staying informed and adaptable is key to success. Hence, the transformative potential of DLT highlights the impact on financial inclusion, payment efficiency, and the broader economic ecosystem.
The Move Towards Tokenization
President of Hedera, Charles Adkins, told BeInCrypto that blockchain technology has emerged as a fundamental force in transforming transactions, lending, and investments. He attributed the success to the inherent capabilities that enable simultaneous access, validation, and record updating.
This innovation is particularly impactful in cross-border payments, trade financing, and end-to-end payment transfers.
It enables banking institutions to conduct near “atomic” international settlements with reduced manual interventions and lower costs. Indeed, such advancements enhance payment models’ efficiency and extend financial services to previously unbanked populations, fostering greater financial inclusion.
“Blockchain technology sets out to enable individual collaboration and allow societies to play a part in determining the future of technological innovation. DLT, for instance, has created new trust layers that enable individuals, enterprises, and governments to generate collective social impact without the risk of bad actors acquiring influence,” Adkins said.
Read more: Deploying Blockchain Infrastructure: Challenges and Solutions
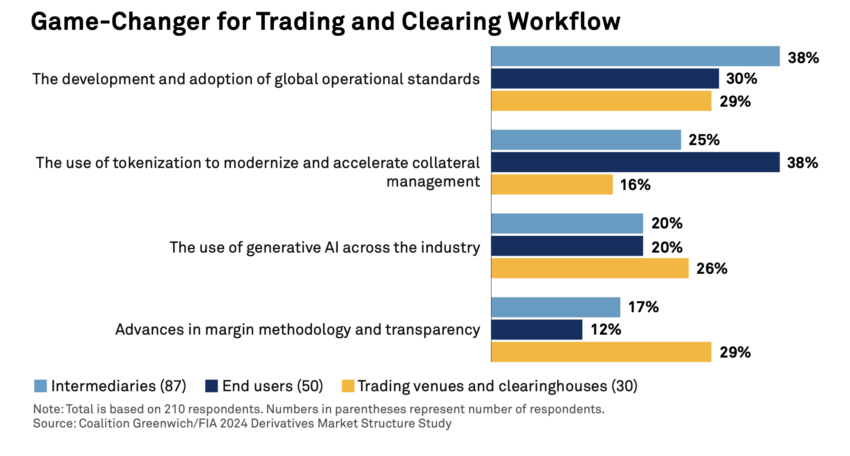
DLT is at the forefront of financial innovations like fractional tokenization, promising to democratize access to wealth opportunities. Indeed, a recent study conducted by Coalition Greenwich revealed that stakeholders in the derivatives sector prioritize the adoption of tokenization. It helps enhance collateral management over implementing generative artificial intelligence (AI).
In fact, for end users, tokenization emerged as the most significant potential innovation in trading and clearing workflows.
“Many large asset managers are working on projects to test the potential for using [tokenization] to move cash and securities more efficiently. From their perspective, the transformation of financial assets into tokens and the use of distributed ledgers to manage transfers could lead to a substantial reduction in time and expense,” analyst at the Coalition Greenwich wrote.
For this reason, Adkins envisions a future where DeFi and traditional finance technologies converge, enhancing the financial system for institutions and individuals.
Blockchain Beyond Financial Markets
DLT’s potential extends beyond financial markets to address pressing issues like climate change and greenwashing. By enabling accurate tracking and reporting of carbon emissions, DLT empowers organizations to optimize their processes, align with environmental standards, and offer transparency to consumers and policymakers.
However, building trust and understanding between developers, policymakers, and the public is crucial to achieve this. Commitment to education, crypto advocacy, and collaboration among Web3 projects exemplify the efforts to ensure security and transparency across public and private sectors.
“DLT plays a vital role in preventing greenwashing attempts by organizations, an issue that has grown in relevance due to difficulties in verifying if companies are adhering to sustainability goals. Because data is publicly available on the distributed ledger, organizations can’t falsify their carbon footprint or make unbacked claims about their sustainability efforts,” Adkins emphasized.
One notable project, as discussed in a study by the University of Copenhagen, involves the use of blockchain technology to create a detailed and transparent record of companies’ carbon footprints. This project, named REALISTIC, allows for the precise documentation of goods’ CO2 emissions throughout their production and supply chain processes.
The implementation of such technology aids companies in complying with new EU legislation that mandates the reporting of carbon footprints. It also paves the way for consumers to verify the environmental impact of their purchases through QR codes.
“[With a pen, for instance] we don’t know the equivalent carbon association which each of its parts… So when you’re looking to procure the various parts of the pen you will know exactly how to weigh which part comes from where, and understand the impact in terms of carbon [footprint],” Chief Revenue Officer at SAP Sustainability Deb Kaplan said.
Read more: Top 9 Eco-Friendly Cryptocurrencies To Invest In
The Climate Ledger Initiative (CLI) is another key player. It focuses on the integration of digital innovations like blockchain, the Internet of Things (IoT), and artificial intelligence for climate change mitigation and adaptation. The CLI supports various use cases and provides a platform for testing digital innovations in real-life scenarios. Therefore, it emphasizes the role of DLT in scaling carbon markets and enhancing their environmental integrity.
Adkins believes the integration of DLT with AI is poised to tackle misinformation and data integrity challenges. As blockchain technology matures, He anticipates its mainstream adoption, unlocking societal and economic benefits, especially in asset management and beyond.
“DLT will allow developers to address challenges with low-quality, biased, and unverified data, providing data-sharing infrastructures that are open to all researchers and developers, and ensuring transparency at every point of the AI data input process,” Adkins concluded.
Staying ahead in the markets requires an unwavering commitment to innovation, ethical governance, and community engagement. By embracing the principles of DLT, individuals and institutions can ensure a confidence and integrity in the digital age.
