DePIN has come to the world, providing the opportunity to create defi projects that reward actions in the physical world. What is this technology about, and how does DePIN work?
Table of Contents
Theoretical studies in cryptocurrencies have long predicted that encryption tools currently implemented in the blockchain will be used on the Internet and impact the physical world sooner or later. Nick Szabo noted at the end of the 20th century that smart contracts can automatically manage physical objects. More than 25 years have passed, and the blockchain is firmly embedded in our lives.
This is primarily due to cryptocurrencies: Bitcoin (BTC) continues to break records and is supported by significant physical infrastructure. At first glance, this confirms an actual physical presence in our world.
However, the boundaries of decentralized technologies continue to expand with the advent of solutions such as DePIN.
What is DePIN and why does blockchain need it?
DePIN meaning a Decentralized physical infrastructure network. Blockchain participants use a public ledger and cryptocurrency to build and maintain specific, real-world infrastructure projects. Simply speaking, DePIN involves using DePIN blockchain to run and sustain decentralized networks of equipment that can serve a common purpose.
This enables the network to be built on decentralized, horizontal connections rather than the hierarchical approach typically seen with large infrastructure projects such as bridges or roads. Building and managing physical infrastructure networks is expensive and complex, so historically, they have been the domain of large corporations or governments with capital and resources.
In contrast, DePIN encourages voluntary cooperation among participants. People can participate in DePIN networks by using their own hardware or purchasing specialized hardware for specific tasks. Options range from simple hard drives to weather stations. However, DePINs are typically built around capabilities that are available to the general public.
Max Thake, co-founder of peaq, explained crypto.news that DePIN uses tokens to incentivize people to use connected hardware to offer services to other people:
“Let’s imagine a smartphone-focused DePIN like Roam Network. The smartphones, owned by regular people, are the hardware component, the data on local connection quality they gather is the goods. Telecom companies looking to improve their services buy this data on a Web3 marketplace, which is where the smart contracts come into play, enabling the value exchange between the supply and demand sides.”
Max Thake, co-founder of peaq
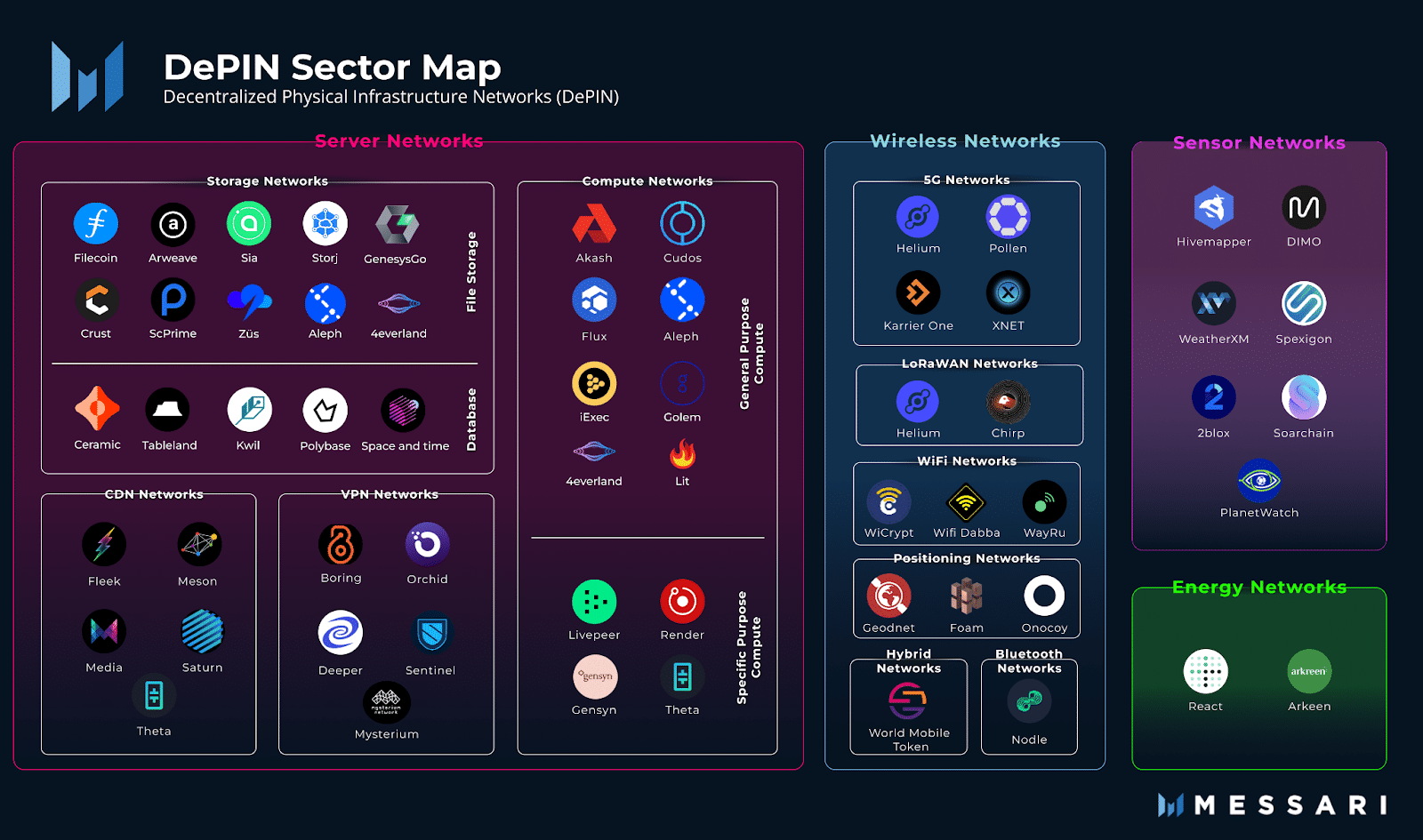
What are the DePIN options?
There are two types of DePINs: Physical Resource Networks (PRN) and Digital Resource Networks (DRN).
PRNs are decentralized networks where providers give hardware resources (such as sensors or internet access), and these resources are tied to a specific location. Their contribution to the network is location-dependent, therefore they are not interchangeable.
DRNs are networks where providers provide resources determined by their function, not location. Here, location does not matter. Examples of such resources include computing power, bandwidth, and storage.
Advantages and disadvantages of DePIN
DePIN can theoretically wholly transform how we manage and interact with physical infrastructure. Using blockchain and smart contracts, this model increases the efficiency and transparency of systems, allowing the community to make decisions independently.
DePIN can be considered a kind of “industrial DAO,” where all participants have equal opportunities and ensure the independence of the infrastructure. The system is flexible and can be scaled horizontally. With the successful attraction of motivated users, the creation of a decentralized physical infrastructure can be significantly accelerated.
The pricing model in DePIN crypto systems is also considered more accessible and fair since infrastructure assets are publicly owned, and the cost of services is determined not by the company’s benefits but by availability. Rewarding participants in the form of tokens allows users to receive regular passive income with the benefit of society.
However, significant disadvantages should be considered:
- Vulnerability to hacks and errors.
- High volatility of tokens.
- There is a need for technical knowledge to maintain a decentralized infrastructure.
Nevertheless, with DePIN, blockchain powers real-world DePIN use cases and value exchanges, it is inherently linked to real-world supply and demand, which makes this segment uniquely positioned for sustainable, healthy growth.
“People won’t stop using navigation apps, ordering food, or using the Web because Bitcoin took a dive. DePIN merges web3 with real value instead of speculation and offers it a chance to live up to its promise of changing the world.”
Looking to the future: What will happen to DePIN in five years?
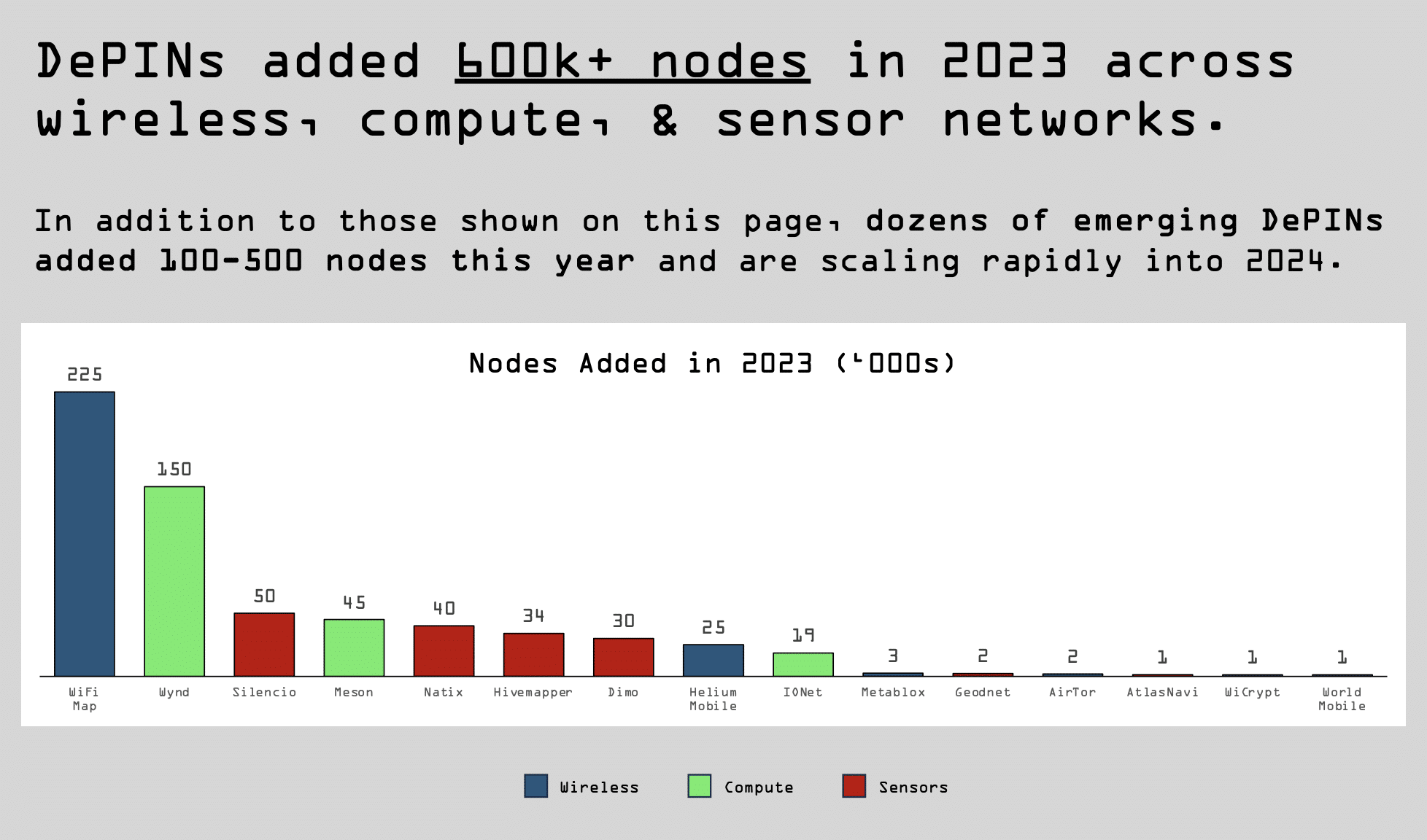
According to Messari analysts, in 2023, the DePIN ecosystem grew to more than 650 projects, and the number of nodes increased by 600,000. Researchers noted the main trends in the development of DePIN in 2024.
Experts believe meme tokens will contribute to massively adopting projects like the BONK airdrop for Solana Saga smartphone users. Analysts also consider Asia to be the region with the most significant potential for the rapid development of decentralized infrastructure, expecting that some of the most influential projects in the sector will appear here from 2024 to 2025.
The first development in the DePIN field appeared about ten years ago. During this time, the number of projects increased significantly. The sector’s market capitalization is more than $20 billion, excluding RWA and blockchain oracles, according to experts from Messari.
Speaking about the future of DePIN, Thake expects it to become an industry staple alongside the entire supporting stack, from DePIN-crowdsourced data for training models to decentralized compute and Web3 federated learning markets for AI agents.
“Some of the most exciting implementations of the DePIN model will be in the energy industry, especially when it comes to green energy, which requires flexible and decentralized grids, while most old-school ones follow the centralized model. People will soon earn by harvesting solar energy and contributing to the power grid.”
However, DePIN projects are not yet popular even among participants in the cryptocurrency industry, let alone the widespread adoption of the concept. Implementing decentralized infrastructure may take time since DePIN faces problems that must be solved. However, experts are confident that this system will play a key role in shaping the future and changing the principles of operation of physical infrastructure.
